types of electronic transitions ppt|UV visible spectroscopy : Clark There are 6 types of electronic transitions that can occur in molecules: 1) σ→ σ* transition, 2) π → π* transition, 3) n→σ* transition, 4) n→π* transition, 5) σ→π* transition, and 6) π→σ* transition. These electronic transitions can be represented . Cappersmall Forums » Tennis . This section of the Cappersmall forum talks about tennis picks, predictions, and betting. Cappersmall provides betting talk, live sports odds, betting information, and articles. Forum cappersmall.com Facebook Followers 2.6K Frequency 28 posts / year View Recent Threads. 8. Mens Tennis Forums » Tennis .
PH0 · Uv spectroscopy
PH1 · UV visible spectroscopy
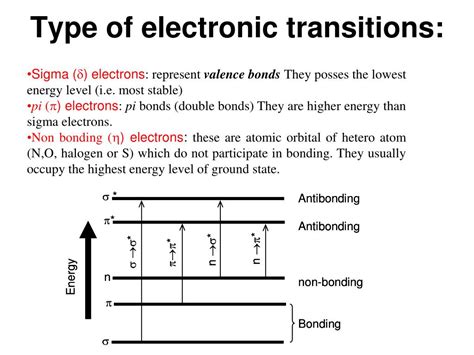
PH2 · TYPES OF TRANSITIONS: In U.V spectroscopy molecule
PH3 · Slide Transitions in PowerPoint [A Beginner’s Guide!]
PH4 · PowerPoint Presentation
PH5 · Part 2.9: Electronic Transitions
PH6 · PPT
PH7 · Electronic transition.pptx
PH8 · Electronic Transitions and Photochemistry
Check if the specific battery PPID (Dell Part Piece Identification) is affected. This step is necessary to identify if your Dell laptop battery is affected. If the battery is subjected to a recall, you are automatically connected to a replacement order form. You need the Dell laptop Service Tag or the battery PPID (serial number) for this process.
types of electronic transitions ppt*******There are 6 types of electronic transitions that can occur in molecules: 1) σ→ σ* transition, 2) π → π* transition, 3) n→σ* transition, 4) n→π* transition, 5) σ→π* transition, and 6) π→σ* transition. These electronic transitions can be represented .Four types of electronic transition are possible. i. σ ⇾ σ* transition ii. n ⇾ σ* transition iii. n ⇾ π* transition iv. π ⇾ π* transition. 2 i. σ ⇾ σ* Transition : An electron in a .Interaction between an electromagnetic wave and the wave function of a molecule/atom/material. Transition between quantized energy states of an . Presentation Transcript. UV-Vis Electronic transitions (UV-vis) Bond vibrations (IR) Nuclear spin (NMR) UV-Vis When UV-Vis light is absorbed by a molecule .Common ones include: C=C Bonds. Example of a transition. -to-C=O Bonds. Example of an n-to-transition. Molecular Orbital Transition Data. In a C=C bond, absorption can lift a .
The main types of electron transitions are σ->σ*, n->π*, π->π*, and n->σ*. Selection rules determine which transitions are allowed. UV-visible spectroscopy is used .
Molecular Spectroscopy Types of transitions:. 1) Electronic (UV-Vis-Near IR) 2) Vibrational (IR) 3) Rotational (microwave). Electronic Absorption Spectra. p → p *.
It describes the electromagnetic spectrum and different regions. UV-visible spectroscopy involves electronic transitions in molecules from ground state to excited .UV visible spectroscopy PowerPoint Presentation. Hello Jablonski Diagram. Types of electronic transitions. We will use the diatomic for our illustration: S0is the g.s. which is a singlet state, S1and . Electronic transition • Electronic transition (UV) measure the probability and energy of exciting a molecule from G.S. to E.S. (or promoting electron from HOMO to LUMO). • For each energy state both .types of electronic transitions ppt Different types of electronic transitions like σ→σ*, n→σ*, π→π*, and n→π* are explained. Instrumentation components like radiation sources, monochromators, sample holders and detectors are briefly outlined. . PPT of seminar on UV Visible spectroscopy, electronic transitions, Instrumentation of Double beam .
Uv visible spectroscopy ppt. UV-VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY The document discusses UV-visible spectroscopy, including the electromagnetic spectrum, types of electronic transitions (σ-σ*, π-π*, n-σ*, n-π*), terms used (chromophore, auxochrome), absorption bands (K, R, B), and Beer-Lambert law. It provides details on . The types of electronic transitions that can occur, such as n→π*, π→π*, and σ→σ* transitions, are explained. The effects of chromophores, auxochromes, and solvents are also summarized. Key concepts covered include electronic excitation and absorption, molecular orbitals, bonding and antibonding orbitals, and the factors that .
electron from a electronic ground state to higher energy state, usually from a molecular orbital called HOMO to LUMO. 19 UV-Vis light causes electrons in lower energy molecular orbitals to be promoted to higher energy molecular orbitals. HOMO LUMO. 20 Electronic transitions. There are following types of electronic transition takes place in UV . There are several types of electronic transitions that can occur when molecules absorb this light. The amount of light absorbed follows Beer's law and is proportional to the concentration and path length of the sample. A UV-visible spectrophotometer consists of a light source, monochromator, sample holder, detector, .
It discusses the basic principles including electromagnetic radiation, interaction of radiation with matter, and electronic transitions. It describes Beer-Lambert's law and how absorbance is directly proportional to concentration and path length. Different types of electronic transitions like σ→σ*, n→σ*, π→π*, and n→π* are explained.
Frank – Condon Principle The electronic transition is fast (10-15 s) with respect to nuclear motions. Transitions where the position and momentum of the nuclei don’t change are favored. J. Michael Hollas, Modern Spectroscopy, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1992. Vibronic transitions where the wavefunctions line up are favored. Ingle .
pair of bonding -electrons. In other words, an unsaturated bond contains four electrons, two of which - electr. ns and two are - electrons. Among these the -elect. ons are the easiest to excite. The transition of a - electrons results in the absorption in t. .

Electronic Spectroscopy.ppt. This document discusses electronic spectroscopy techniques such as ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy and chiroptical spectroscopy. It describes how UV-vis spectroscopy can be used to study electronic transitions in molecules, detect functional groups, and perform quantitative analysis. . AI-enhanced description. The document provides information about electronic spectra and terms for carbon p electrons and transition metal d electron configurations. It discusses: 1) Possible terms that arise from carbon's 2p electrons, including 1D2, 3P2, 3P1, 3P0 and 1S0 terms. Hund's rules are used to determine the . π- π* transition The transition or promotion of an electron from a π bonding orbital to a π antibonding orbital is designated π- π* transition.These type of transitions occur in compounds containing one or more covalently unsaturated groups like C=C,C=O,NO2 etc., π- π*Transitions require lower energy than n - σ * transitions. n - .Types of transitions related to the metal ion: d-d transitions: d-d transitions are electronic transitions that occur between the molecular orbitals (MOs) that are mostly metal in character: specifically, the orbitals that we think of as the d-orbitals of a transition metal complex.These transitions are useful in determining the energy of splitting and .
types of electronic transitions ppt UV visible spectroscopy M. This document discusses the six main types of atomic fluorescence transitions: 1) Resonance fluorescence occurs when the emitted wavelength equals the absorbed wavelength. It produces the most intense fluorescence but scattered light is a drawback. 2) Stokes direct line fluorescence occurs when the emitted wavelength is .
It discusses how UV-visible spectroscopy involves exciting electrons from lower to higher orbital energies using electromagnetic radiation between 200-800nm. The absorption of radiation is dependent on the structure of the compound and type of electron transition. The main types of electron transitions are σ->σ*, n->π*, π->π*, and n->σ*. Some key points: - UV-Vis spectroscopy involves promoting electrons from the ground state to excited states using electromagnetic radiation in the ultraviolet and visible regions. - Different types of electronic transitions are possible including π-π*, n-π*, and σ-σ* transitions. The π-π* and n-π* transitions fall within the UV-Vis range. There are three main types of electronic transitions that can occur in organic molecules: 1. σ → σ* transitions: These involve promotion of electrons from bonding σ orbitals to antibonding σ* orbitals. They require high energy in the far UV region (below 200 nm) and are usually not observed for organic compounds. 2.
Download ppt "Part 2.9: Electronic Transitions". Absorption spectroscopy Types of transitions Outline Absorption spectroscopy Types of transitions atomic molecular d-d transitions Transition moment Microstates Correlation diagrams Tanabe-Sugano diagrams Selection rules.
Types of electronic transitions a) 𝜎−𝜎* Transition: transition of an electron from bonding sigma orbital (𝜎) to anti-bonding sigma orbital (𝜎*), is represented by 𝜎−𝜎* transition. For example, alkanes because in alkane all the atoms are held together with sigma bond.
Bruges (/ b r uː ʒ / ⓘ BROOZH; French: ⓘ; Dutch: Brugge ⓘ; German: Brügge [ˈbʁʏɡə] ⓘ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country.It is the sixth most populous city in the country. The area of the whole city amounts to more than 14,099 hectares (140.99 km 2; 54.44 .
types of electronic transitions ppt|UV visible spectroscopy